With increasing age, a herniated disc usually develops when the inner core of the disc loses its gelatinous consistency and thus the function of a buffer. This causes the fibrous ring and preferably the posterior longitudinal ligament to overstretch and loosen. When lifting heavy objects, especially with the upper body bent forward, or other typical incorrect or excessive loads on the spine, the gelatinous core can advance into the spinal canal and press on the surrounding nerve tissue. In rare cases, injuries or accidents can also lead to a herniated disc.
In addition to age-related signs of wear and tear, obesity, permanent incorrect loading of the spine and excessively weak back muscles play a role in the development of a herniated disc.
The symptoms of a herniated disc depend on its location and severity and on which neighboring nerve structures are affected. A herniated disc does not necessarily cause pain, but the acute stabbing pain is a classic symptom. The pain may be limited to the lumbar spine or radiate into the legs to beyond the knee region. Often, sensory disturbances (numbness, tingling) and muscle weakness occur in the affected region. Coughing and sneezing intensify the symptoms. In the case of a herniated disc in the area of the cervical spine, the symptoms appear in the arms and hands.
In rare cases, due to a herniated disc, there are disturbances in defecation and urination associated with numbness in the anal and genital areas and on the inner thighs. These symptoms are considered an emergency and require immediate surgical treatment.
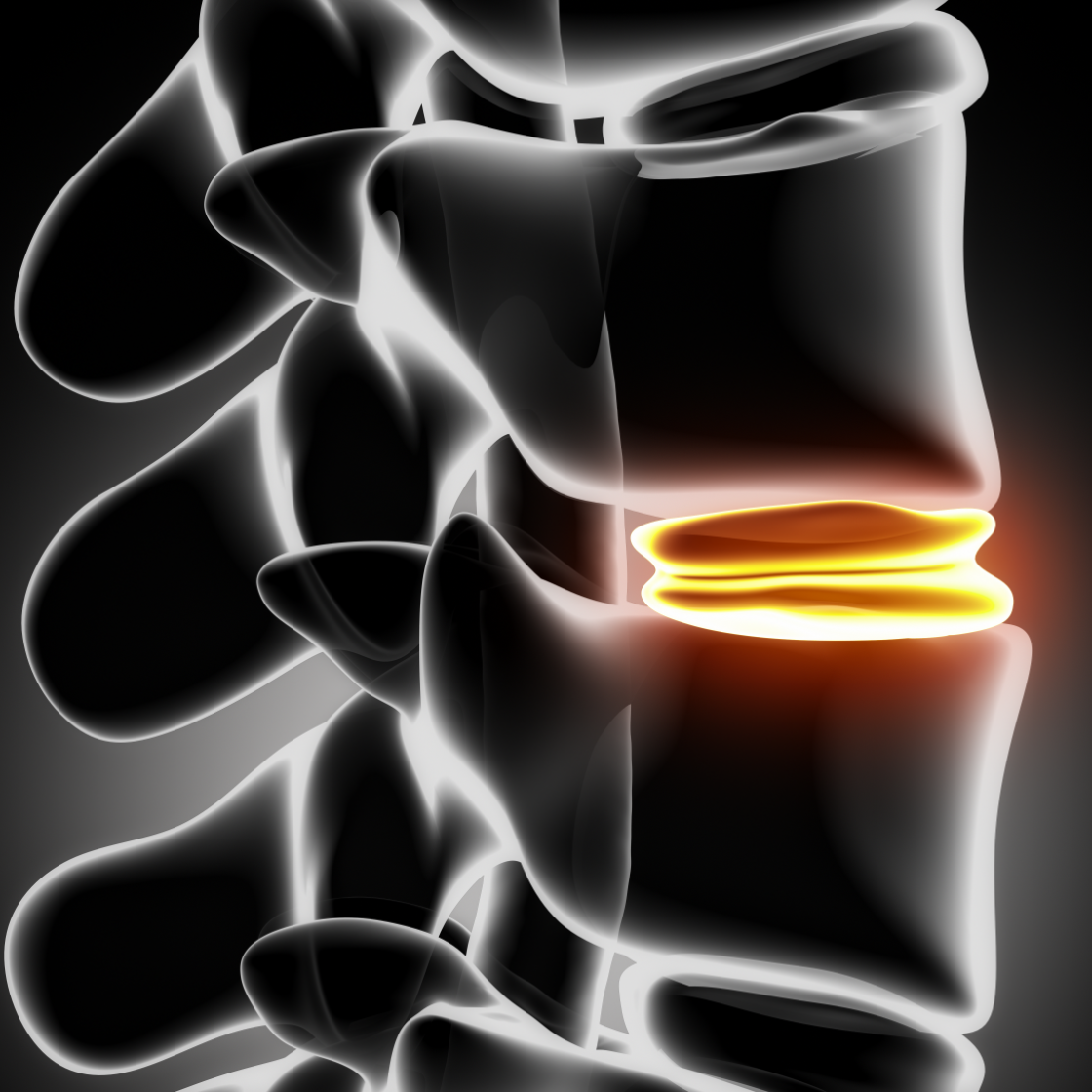
Under certain conditions, there is the possibility of so-called endoscopic surgery in the case of a lumbar disc herniation (herniated disc in the lumbar spine). In this case, the herniated disc can be removed through a skin incision of less than one centimeter either in the area of the flank or the lower back. This procedure is very gentle for the patient, as there is no need to open the spinal canal over a large area. This almost completely reduces the scarring often feared by the patient. Due to the very gentle surgical procedure, the patient can usually leave the hospital after only 4 days.
However, they are not suitable for all types of disease. Primarily, simple and fresh disc bulges and herniated discs without sequestration are considered. Pre-operated patients cannot be treated with this method.
Further links to the spine
